Insufficient mine investment could drive sustained shortages and price volatility, warns Wood Mackenzie
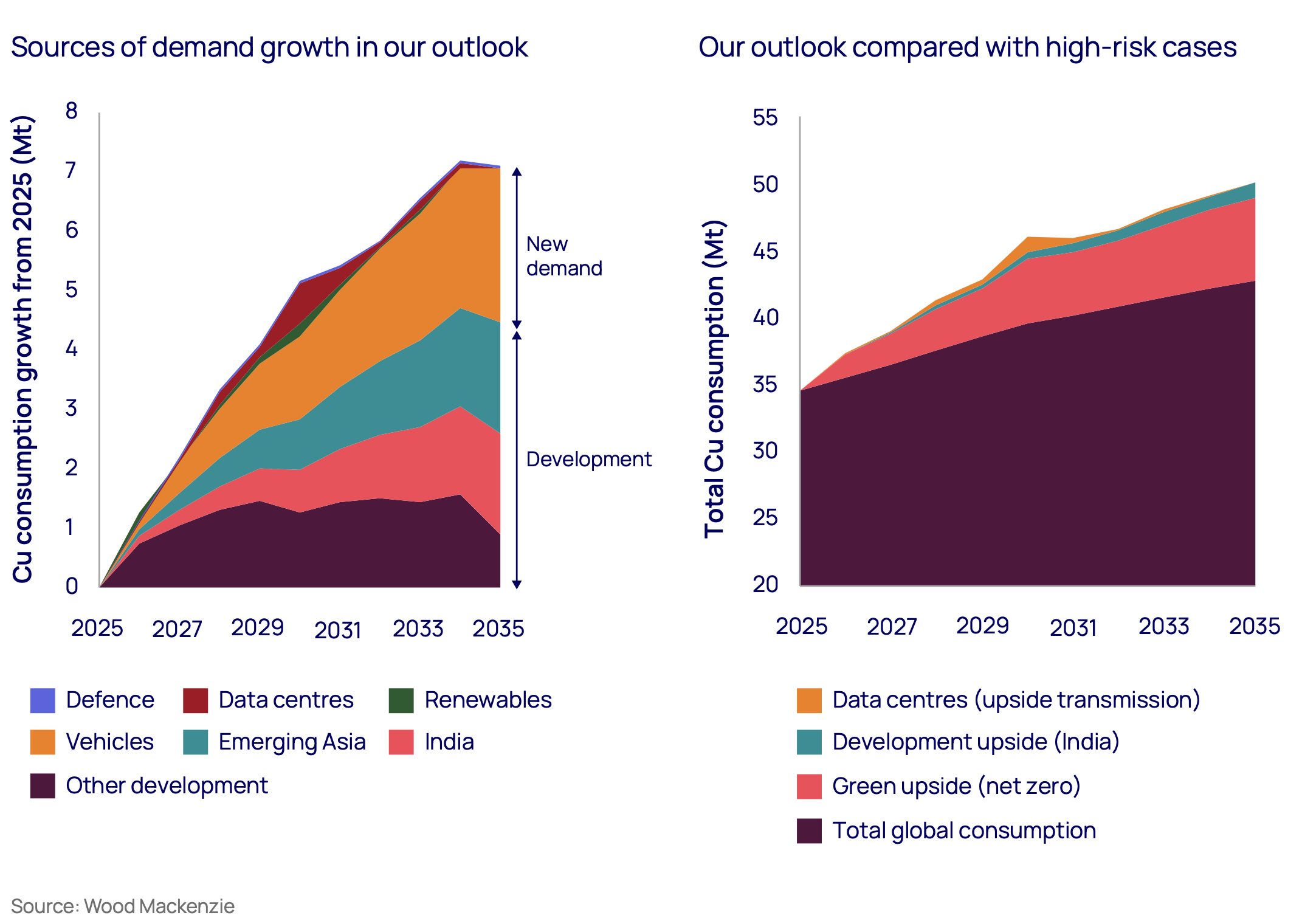
LONDON, HOUSTON, SINGAPORE, 15 October 2025 – Global copper demand is set to surge 24% by 2035, rising by 8.2 million tonnes per annum (Mtpa) to 42.7 Mtpa, according to a new Horizons report from Wood Mackenzie, ‘High-wire act Is soaring copper demand an obstacle to future growth?' Growth will be driven by traditional economic development alongside new structural demand from electrification and digitalisation.
While this growth trajectory seems certain, Wood Mackenzie warns that four powerful disruptors could amplify demand and price volatility beyond expectations. Together, these disruptors could add an extra three Mtpa, or 40% of total copper demand growth, by 2035.
Simultaneous increases in copper demand in multiple sectors
Data centres emerge as volatility wild card
Among these disruptors, data centres represent the most unpredictable variable in copper demand forecasting. Artificial intelligence is set to consume an additional 2,200 TWh of electricity by 2035, according to global data centre projects tracked by Wood Mackenzie's Power team. This will lift copper demand for grid infrastructure alone to 1.1 Mtpa by 2030.
The report noted that as copper represents less than 0.5% of total project costs, data centre developers remain largely indifferent to its price movement. A sudden surge in construction could therefore trigger price spikes of 15% or more, rapidly depleting inventories and intensifying volatility.
“Data centres create inelastic demand in the market,” said Peter Schmitz, at Wood Mackenzie. “When developers require copper for the expansion of data centres, it is used will little concern for the copper price. This dynamic in a nascent sector makes data centres an unpredictable and volatile source of demandthis decade.”
Energy transition reshapes structural demand
Beyond AI-driven demand, the broader energy transition is fundamentally reshaping copper consumption patterns. The shift to renewable energy systems will require an additional two Mtpa of copper supply over the next decade, according to Wood Mackenzie. The geopolitical implications of copper supply chains have become increasingly apparent as nations seek to reduce reliance on volatile energy imports. The report noted that copper demand from the sector is projected to climb from 1.7 Mtpa today to 4.3 Mtpa by 2035, an annual growth rate of 10%.
“Each electric vehicle contains up to four times more copper than a conventional car,” said Peter Schmitz. “As battery technologies advance, copper demand intensity across charging infrastructure and power systems will remain high. By our forecasts, EV-related copper demand is set to double by 2035, cementing the metal's role at the heart of the global energy transition.”
Asia's industrialisation accelerates copper growth
India and Southeast Asia are emerging as powerful engines of copper consumption, with their rapid industrialisation expected to add 3.3 Mtpa of demand by 2035. This translates to average annual growth rates of 7.8% and 8.2%, respectively, according to the latest Horizons report
If these economies replicate even half of China's historical growth path, their construction and power sectors alone could require an additional 5.4 Mtpa of copper. With per-capita copper use still far below global averages, these markets represent substantial long-term upside for demand.
Defence spending adds a new layer to demand dynamics
The fourth disruptor stems from shifting geopolitical priorities. Europe's decision to raise defence spending to 3.5% of gross domestic product (GDP) amid Russia's invasion of Ukraine and shifting global security priorities adds only modest direct copper demand of around 25 to 40 ktpa over the coming decade. However, the broader impact will be felt through infrastructure resilience and modernisation.
“Rising defence budgets are creating a quiet but meaningful source of incremental copper demand,” said Peter Schmitz at Wood Mackenzie. “While the headline numbers for military hardware appear limited, the supporting infrastructure, including hardened power networks and communications, is also copper intensive, adding scale to copper demand for defence through what appears to be normal development. This dynamic adds another layer of pressure to an already tight supply environment.” Defence firms worldwide are signalling expansions across fighter programmes, missile-tracking systems and ammunition production, with infrastructure following suit, reinforcing copper's growing role in the industrial–military complex.
Supply challenge intensifies amid climate pressures
Meeting this demand growth will require more than eight Mtpa of new mine capacity and 3.5 Mtpa of additional scrap by 2035. Wood Mackenzie estimates the industry may need to lift its baseline assumption for annual mine disruptions from 5% to 6%, effectively removing 250–300 kt from the market each year and tightening supply further.
In a supply-constrained environment, the convergence of these four disruptors could result in prolonged periods of high prices and unpredictable market fluctuations.
“Copper has become the strategic bottleneck of the global energy transition,” said Charles Cooper. “From Detroit to Shenzhen, the impacts of commodity supply chain disruptions and the industry's inability to deliver will be acutely felt. If governments and investors fail to act, we risk turning the metal of electrification into the metal of scarcity.”
Editor notes:
Read full report here: High-wire act: is soaring copper demand an obstacle to future growth? | Wood Mackenzie